Home » Erectile Dysfunction in Young Men: What Are the Causes and Solutions?

It is a very common sexual disorder found in a large number of men. Though generally associated with males above the age of 40, reports of ED have progressively been occurring among erectile dysfunction under 40 as well. The increase in the number of youthful patients can be related to leading a sedentary lifestyle and increased work stress. ED impacts men physically and psychologically. Men become strained and anxious once they realize that they are unable to achieve an erection or attain pleasure during sexual activities. Young males are becoming more concerned about their ED issues because of the growing incidence of this male health problem. Erectile dysfunction is frequently considered a consequence of poor sexual efficiency, emotional or psychological issues. However, the problem may also be linked to underlying health problems, restricted blood flow, and other factors. The lack of understanding contributes to the topic being highly stigmatized. This review is intended as an overview of a variety of illnesses, lifestyle choices, and other factors that could contribute to erectile dysfunction in young men.
Erectile dysfunction is now a major general health concern. ED is defined as an inability to achieve a partial erection often, an inability to achieve a rigid erection, or inability to sustain the erection for an extended period of time if a rigid erection is partially achieved. Younger men also increasingly suffer from erectile dysfunction under 40. This elevated incidence of ED diagnoses among younger men could simply be caused by greater awareness of erectile dysfunction in this age category. A large number of the men studied had actually never engaged in sexual intercourse. Mixed messages, exaggerated ideas regarding penile size, broader sexual discontent, attitudinal sexism, and attitudes that redefine the dehumanization of male sexual desires as a natural rule all have the potential to create conflict in enduring, communicative arrangements. Allowing men to share in societal efforts to reduce stigma and discriminatory practices against all people with sexual problems is a radical cornerstone.
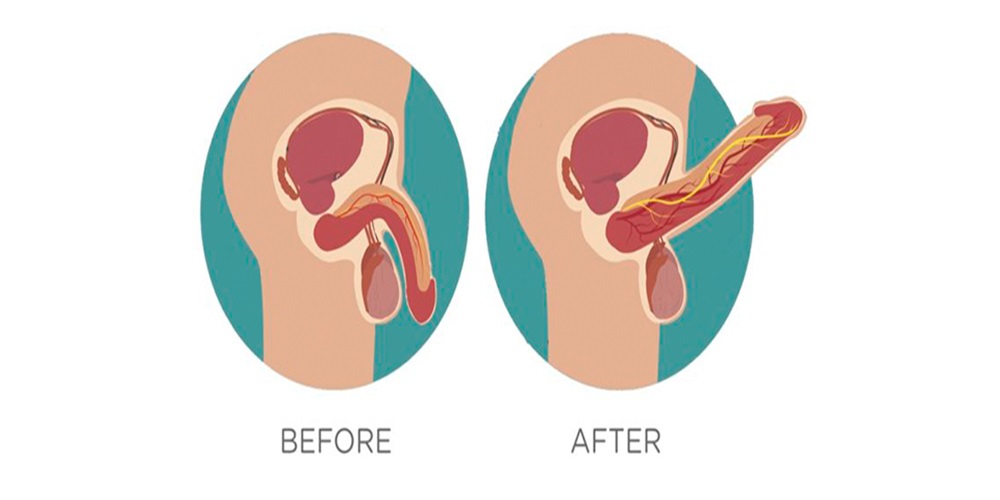
Erectile dysfunction (ED), defined as the consistent inability to achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for good sexual performance, is influenced by several factors. For young men, anxiety regarding sexual performance or the fear of failing to attain and sustain an erection is a psychiatric aspect of ED. Depressive symptoms and relationship issues may stem from their erectile dysfunction under 40. However, there are physical components of ED that may influence penile erection. The simplest young men erectile dysfunction causes are linked to lifestyle. Common risk factors include obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, and cardiovascular diseases, all of which can result in ED. Additionally, ED is associated with obstructive sleep apnea and hypogonadism or a low level of testosterone. Excessive consumption of coffee or soft drinks, physical inactivity, and the use of illicit drugs or tobacco can also predispose a man to various lifestyle conditions affecting penis function. Tobacco use, more importantly, has been demonstrated as a risk factor for ED due to its implication in reduced blood flow to the penis.
This is a kind of hormone imbalance, leading to the partial loss of erectile function in men. ED solutions for young men who take medications that have sexual side effects have a risk of developing erectile dysfunction. Decreased testosterone production promotes obesity, and vice versa, enabling a cycle of ED. Psychosocial and behavioral factors that can lead to ineffective sustained erection are influenced by either a psychological effect or a physiological one. Hormonal imbalances, in combination with psychosocial and lifestyle conditions, can hinder the optimal physiological response and essentially complete the cycle of physical dysfunction to perpetuate erectile dysfunction in the young patient. These two processes affect and enhance each other, creating a tangling loop of causality.
A proper diagnosis of the first symptoms of erectile dysfunction is critical for ED solutions for young men. A detailed medical history helps health experts determine the root young men erectile dysfunction causes. Physical examination may bring to the fore the following issues: hypogonadism, Peyronie’s disease, peripheral vascular disease, vascular access, neurological disease, cavernosal disorders, or endocrine diseases. Nicotine, drug, cannabis, alcohol, and even caffeine abuse can also become part of the evaluation. Anxiety, low self-esteem, low desire, low relationship satisfaction, and mixed premature ejaculation caused by inadequate cholesterol levels may also be indicators for erectile dysfunction in young men. Erectile function can be assessed using questionnaires and objective tests. The latter may refer to the following tests: angiography, arteriography, Doppler resonance, magnetic resonance angiography, computed tomographic angiography, penile ultrasonography, penile arteries assessment by vesiculography, cavernosometry, and cavernosography, digital stimulation, and urine levels of nitric acid.
Relaxation test of cavernosa and radioactive isotope penile blood flow. For a healthy erection, a comprehensive evaluation of the sexual and psychological history of the patient is necessary. This may sometimes present special or complicated life events, and assessment of the physical and psychological states, the ability to become aroused, to attain flow in the penis, to persist in erections, and ED solutions for young men, as well as partnership and family support, is key for emotional and sexual dysfunction in men. Identifying problems within mental distress can help to identify individuals who need special treatment. Proper examination of sexual and psychological evaluations offers insights to check how both are impaired if sexual function occurs and medical treatment is necessary. Health experts need to combine psychological and professional evaluation, especially in evaluating cases with lifelong disorders, and relatively young patients, rather than relying on the experience of sexual dysfunction in the whole population. Of course, effective communication between the care teams and patients is important to achieve this goal. Patient health history is important, so make sure young people do not hesitate to share what they want. Both their presentation and therapies will benefit from these young people and eventually use their assessment of medication. Only one death could be taken to ensure better care and health outcomes, only to highlight the simple issue. Even if erectile function is not a sign of potential illness, a complete examination is vital. Finally, the ability to address the disease can be improved in the future.
Treatment and Management A range of pharmacological treatments are available for ED, with the most commonly used being PDE5 inhibitors. Studies have found the use of these drugs to be effective in restoring in most Erectile Dysfunction solutions for young men. Thus, monotherapy with the lowest possible doses is the general recommendation. Psychological treatments are advised to address psychological factors in erectile dysfunction under 40 and to provide a more holistic approach to erectile dysfunction treatment. The most effective treatment options include cognitive behavioral therapy, sex therapy, couples therapy, sensate focus exercises, and guided masturbation training. The management, however, of a young man living with ED should also include all pharmacological treatments and psychological counseling with concomitant lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle modification plays an important role in the management of ED. Encourage young men to adopt health-enhancing approaches, including heart-healthy diets and physical activities to maintain ideal body weight. Avoid excessive stress and improve sleeping habits to help maintain general health.Young men in their 20s should be educated about the risks of steroid use in bodybuilding. There are alternative treatment ED solutions for young men, although caution should be exercised when choosing a device or procedure because there is a lack of evidence to support their routine use in this age group. A comprehensive, holistic approach to the young man with erectile dysfunction is advised. Lifestyle changes, psychological treatment, and pharmacological choices should be tailored to individual needs. Prevention and early-onset ED intervention may avoid potentially greater intimacy and psychological issues in later years.
Conclusions erectile dysfunction in young men should be encouraged to seek medical advice and see a practitioner specializing in sexual health. The young man with ED needs a thorough evaluation as the underlying pathology may be indicative of other serious health issues. Treatment may need to be multifactorial in the majority of cases. Most men ultimately respond to PDE5 oral agents, but their impact on ED in the young man is not fully clarified. Psychological treatment and patient education are important for young men as well as reassurance. Abstaining from drug and alcohol abuse is wise, as is reducing weight and increasing exercise with appropriate healthy eating and drinking habits. It is particularly important to engage this last group of young men in effective health promotion strategies. They can inform their peers and have the potential to rescue the next generation of young men from the scourge of erectile dysfunction.
Hello!