Home » DHT and Hair Loss: How This Hormone Causes Thinning and Baldness

Hair loss affects millions worldwide, but few people understand the true biological cause behind most thinning and balding. The key culprit is DHT, scientifically known as dihydrotestosterone — a powerful androgen that plays a central role in male and female pattern baldness.
This comprehensive guide explores the connection between DHT and hair loss, explaining how the DHT hormone functions, why it affects certain people more than others, and what modern science says about DHT blockers, treatments, and prevention strategies.
If you’re struggling with DHT baldness, receding hairlines, or DHT hair thinning, this article provides clear, medically informed answers.
DHT is a derivative of testosterone produced by the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. While essential for male development during puberty, high levels of DHT later in life can damage hair follicles.
Once DHT binds to receptors at the root of the hair shaft, it begins to shrink the follicle — a process called follicular miniaturization. Over time, this leads to:
This is why what causes hair loss in most adults is directly linked to DHT hormone sensitivity, not aging alone.
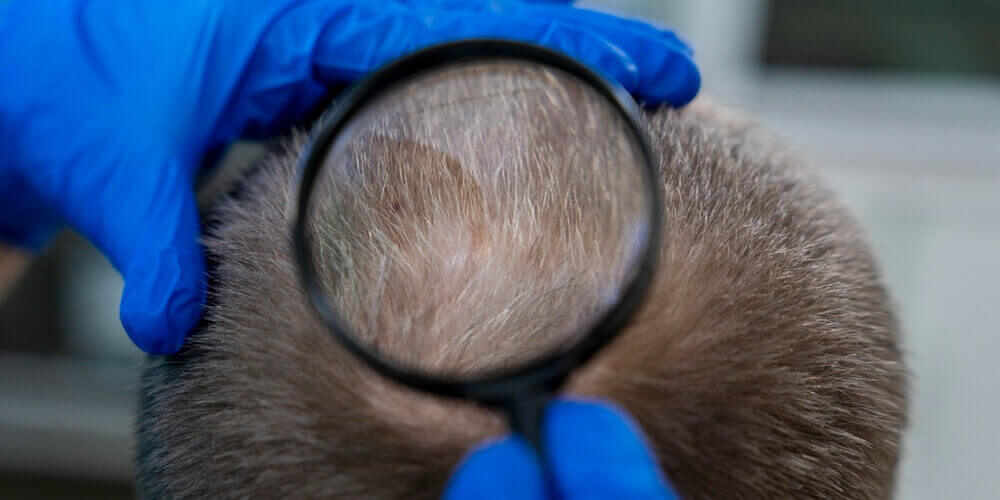
Not everyone exposed to DHT loses hair. Genetics determine whether your hair follicles are sensitive to it.
People with a family history of male and female pattern baldness typically inherit follicles that overreact to DHT. This genetic predisposition explains why:
Your sensitivity, not your hormone levels, is the real driver behind progressive thinning.
In men, DHT is the primary cause of:
This pattern is known medically as androgenetic alopecia. DHT restricts blood supply to the follicles, causing the top of the scalp to weaken first — while the sides and back remain genetically resistant.

Women also experience DHT-related shedding, but the pattern differs. Instead of receding, women usually notice:
Women typically maintain their hairline, but hormonal hair loss becomes more noticeable after:
Even slight elevations in DHT can trigger shedding in DHT-sensitive women.
Common warning signs include:
Catching DHT hair thinning early dramatically increases the success of treatment.
The DHT hormone attaches to receptors in hair follicles, gradually shrinking them through a process called miniaturization. This leads to weaker, thinner strands and eventually prevents new hair from growing entirely. Over time, this hormonal sensitivity creates what is widely known as male and female pattern baldness. Understanding how DHT and hair loss are connected is the first step toward choosing effective treatments, such as DHT blockers, lifestyle adjustments, and medical therapies that help preserve existing follicles and slow further thinning.
There are several ways to lower DHT levels or block its effect on hair follicles. The most effective include:

Prescription treatments slow or stop miniaturization by lowering DHT levels in the scalp.
Widely trusted medical options include:
These medications target the 5-alpha reductase enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT.
For those who prefer non-oral solutions, topical treatments offer a localized approach with fewer systemic effects:
These help reduce DHT directly at the follicle.
While not a DHT blocker, Minoxidil boosts blood flow, extends growth cycles, and thickens weakened strands. When combined with DHT control, results improve significantly.
Platelet-Rich Plasma injects growth factors into the scalp to stimulate regrowth. It is especially effective when DHT has caused moderate thinning but not complete follicle death.
Although lifestyle changes cannot eliminate DHT entirely, they can help reduce inflammation and stress on the follicle:
A holistic approach supports hair density over time.
When DHT has already destroyed follicles, no medication can revive them. In these cases, hair transplantation becomes the gold-standard solution.
Modern techniques such as FUE and DHI allow surgeons to extract DHT-resistant hairs from the back of the scalp and implant them into thinning areas for permanent results.
If your hair is not responding to topical or oral treatments, a transplant may be the most effective long-term option.
Zaren Health specializes in advanced hair restoration treatments tailored to individuals suffering from DHT and hair loss. With expert surgeons, modern FUE/DHI technology, and comprehensive hormonal evaluations, Zaren Health offers long-lasting solutions for those experiencing DHT baldness, hair thinning, or hormonal hair loss. Patients receive personalized treatment plans, including DHT-blocking therapies, PRP sessions, and surgical options when needed — ensuring natural, healthy, and permanent results.
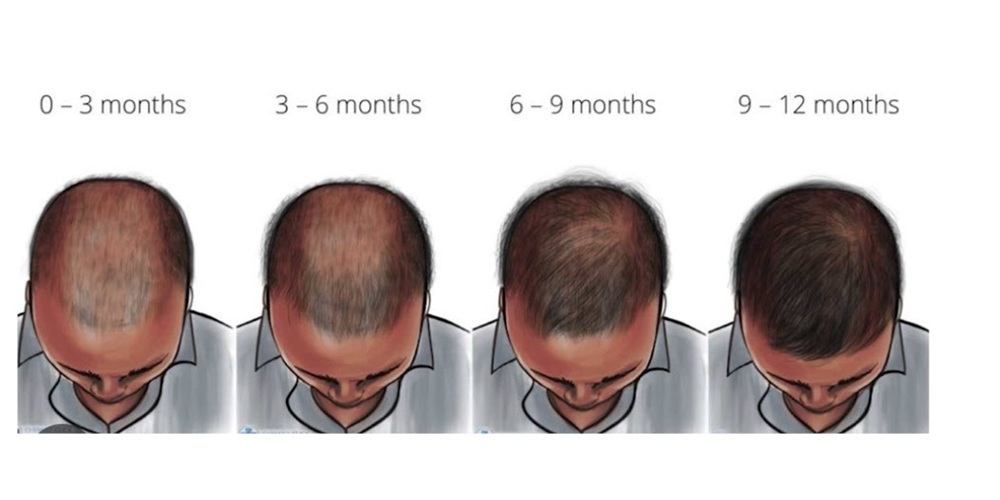
DHT cannot be eliminated permanently, but medications can maintain lower levels as long as treatment continues.
No. Stress, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal changes, and autoimmune conditions can also cause shedding. However, DHT is the primary cause of pattern baldness.
Oral blockers may have mild side effects for some users, while topical versions offer similar benefits with fewer risks.
Yes — if treated early. Miniaturized follicles can regrow when DHT is controlled and blood flow is restored.
Absolutely. Women experiencing pattern thinning or postpartum shedding often respond well to topical anti-androgens and medical treatments.