Home » Cirugía de corrección de mamas tuberosas: cómo funciona y qué esperar

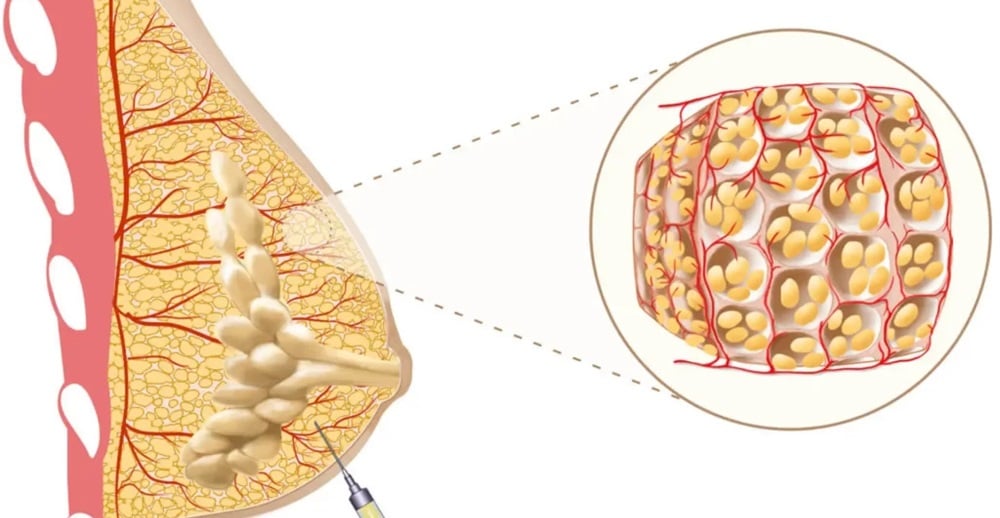
Liposucción: Muchas mujeres con tumores mamarios tienen una forma de constricción del tejido adiposo que se puede tratar con liposucción para liberar la base del seno y crear una forma más natural. Los senos accesorios grandes y largos pueden ser buenos candidatos para una reducción de grasa mediante liposucción simple. Aumento de senos: Expansión de tejido en una o dos etapas para estirar las constricciones anulares duras del seno y crear un nuevo pliegue de sujetador suave y normal. Los implantes se reemplazarán después de que se hayan quitado los expansores de tejido en un procedimiento ambulatorio.
La recuperación después de la cirugía de mamas tubulares tiene en cuenta algunas cosas que se deben tener en cuenta, que incluyen: Inmediatamente después de la cirugía, se la llevará al área de recuperación donde la enfermera la controlará. Al igual que con cualquier otra cirugía, se siente dolor para el cual se administra medicación para aliviar el malestar. Por lo general, al principio se espera algo de decoloración, hematomas e hinchazón. Se le dará el alta el mismo día para que alguien se quede con usted durante las primeras 24 a 48 horas, como es común en la mayoría de las cirugías. La mayoría de los pacientes serán vistos una semana después, luego cada dos semanas para controlar el progreso hasta que se recupere por completo. Durante las semanas siguientes a su cirugía de corrección de mamas tuberosas, las líneas de incisión continuarán sanando. Es importante que siga todas las instrucciones que le den. En ocasiones, puede parecer que las cicatrices empeoran antes de empezar a mejorar. También se le proporcionarán pautas sobre los cuidados posoperatorios destinados a prevenir infecciones. Se espera que después de la cirugía de mama tubular, pueda aparecer algo de hinchazón, que puede durar varias semanas. La hinchazón disminuirá con el paso del tiempo y, una vez que las incisiones hayan cicatrizado, comenzará a ver los resultados finales. Tomar vitaminas, incluidos otros suplementos que hayan demostrado ser beneficiosos para la cicatrización, puede ayudar a un paciente a limitar su proceso de recuperación. La recuperación total de la cirugía de mama tubular se producirá a un ritmo individual. Su cuerpo puede tardar semanas o meses en recuperarse por completo, dependiendo de los cuidados que reciba durante la recuperación. A la mayoría de los pacientes se les recomienda caminar al regresar a casa y, por lo general, pueden reanudar las relaciones sexuales en aproximadamente dos semanas. Dependiendo del tipo de cirugía realizada, durante al menos dos semanas, los pacientes deben evitar cualquier actividad que pueda provocar un aumento repentino de la frecuencia cardíaca y la presión arterial. Se puede realizar una ergometría de ciclo ligero después de tres semanas. Haga arreglos para que un amigo o familiar esté disponible para ayudarla con las actividades de la vida diaria durante los primeros días después de la cirugía. Es bastante común, mientras los senos se curan, experimentar cambios de humor, como sentirse deprimida, llorosa, enojada, etc. Algunas mujeres incluso notan que tienen falta de concentración, entre otras cosas. Esto puede deberse a la reacción del cuerpo a la anestesia y puede demorar algunos días o algunas semanas. Muchas mujeres se quejan de falta de aire, que también puede deberse a la reacción del cuerpo a la anestesia.
Toda cirugía plástica debe comenzar con un entendimiento mutuo de las expectativas del paciente. El tratamiento quirúrgico sólo puede ser tan exitoso como los objetivos establecidos al principio. El funcionamiento de la cirugía de mamas tuberosas puede ser bastante complejo, tener objetivos claros es un indicador importante para un resultado realista y exitoso. Sin embargo, las expectativas deben moderarse con un entendimiento de la variabilidad en la cicatrización del tejido. La rigidez y la hinchazón del tejido son necesarias en todas las cirugías de mama, pero particularmente en la reconstrucción de mamas tuberosas. Los implantes mamarios ampliamente utilizados pueden tardar su propio tiempo en asentarse. Algunos implantes se asientan perfectamente al día siguiente de la cirugía, y otros necesitan un suave masaje por parte del cirujano para cambiarlos a la posición correcta en las primeras semanas posteriores a la cirugía. Ocasionalmente, se necesita hacer un mayor empuje en el bolsillo en una etapa posterior.
La posición del implante mamario no depende sólo de la habilidad del cirujano; las variables incluyen las diferencias anatómicas y de tejido en cada paciente. Las variables anatómicas no sólo predicen el resultado final, sino que también pueden reducir el riesgo de complicaciones si se abordan adecuadamente durante la cirugía. Un daño tisular involuntario durante la disección puede frustrar el mejor plan. Pueden ocurrir más complicaciones cuando un paciente tiene afecciones concomitantes como el tabaquismo y la obesidad. Quizás lo más importante es la variación de los seres humanos desde las perspectivas emocional, psicológica y filosófica. No todos los seres humanos tienen una concepción idéntica de lo que se ve bien y hermoso. A algunos les gusta la plenitud superior, algunos prefieren la plenitud inferior y algunos prefieren la plenitud media. Lo que invoca simetría y equilibrio en una persona puede repeler a otra. Lo que se ve bien para algunos puede ser repugnante para otros. En consecuencia, la experiencia muestra que las respuestas individuales a cómo funciona la cirugía de mama tuberosa pueden ser únicas. A pesar de la amplia gama de variables que contribuyen al resultado, un porcentaje significativo de pacientes que se someten a una corrección de mama tuberosa calificaron su resultado como bueno o muy bueno. La diferencia de tamaño observada antes de la cirugía a menudo todavía se aprecia visualmente después de que se realiza la cirugía para corregir dos afecciones opuestas. Los cirujanos esperan corregir estas afecciones para que se unan, pero en ocasiones, tardan un poco en completar el viaje desde sus posiciones opuestas. El cumplimiento del plan elaborado puede minimizar la frustración si llegara a ocurrir, pero una comprensión realista es que el mejor plan se perfecciona el día en la sala de operaciones, cuando la anatomía exacta del cuerpo puede finalmente ser expuesta por primera vez. Un poco de paciencia con respecto al asentamiento de un implante más grande y la elevación pequeña de otro puede marcar una diferencia crucial en las experiencias del paciente en ambos lados de la mesa de operaciones. La contribución constante de cada uno puede proporcionar los mejores resultados.