Home » Laminate vs. Composite Veneers: Pros and Cons of Each Option
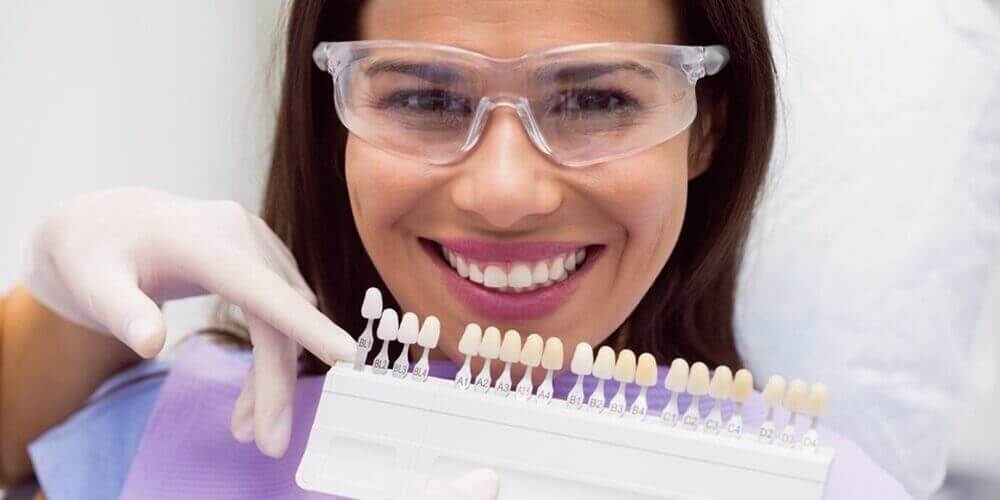

Dental veneers have become quite a useful tool in the dentist’s inventory. They are thin veneers vs thick veneers layers of material especially designed for your teeth and are used to replace enamel. Veneers are usually used in cosmetic dentistry and are effective in correcting many aesthetic issues a patient might have with his or her teeth. They are a quick, painless, and relatively non-invasive solution to many very common dental problems, such as discolored, chipped, fractured, misaligned, or uneven teeth, which may have developed dark spots after root canal treatment, between teeth, or which are too small or too big. Veneers are made in such a way as to look and feel just like your natural teeth. Originally fabricated out of composite vs porcelain, they can now also be made out of composite resins, which are stronger and last longer. They are made in dental laboratories according to prescriptions transmitted by dentists, and because of manufacturing technology, they have become extremely resilient. Veneers can now last for thirty years and are made not to fall off.
Thanks to technology, it has also become very easy in recent years to fabricate them in exactly the color, shape, and form desired by the patient and as indicated by the dentist. Also, patients now have two very accessible solutions when it comes to dental veneers:
1) Laminate vs composite veneers, which are very thin veneers vs thick veneers shells of composite vs porcelain used to recreate the natural look of teeth while also providing strength and resilience.
2) Direct composite veneers, which are built up inside the dentist’s mouth and can be polished right away, therefore requiring only one dentist visit instead of two, and consequently costing around half the price of laminate veneers. The fixed type of veneer is called a laminate, while the built type is referred to as a composite veneer. Both are becoming more and more popular. As a result, it is useful to explore the differences between the two in an objective way. This is what this essay aims to do.
The characteristics of laminate veneers are linked to the type of best veneer material they are made of and therefore emerge as their main advantage. Typically, such veneers consist of several thin layers of composite vs porcelain, which resemble natural tooth enamel. Like natural enamel, laminate porcelain possesses high translucency due to its ability to transmit light partially. This is the main feature that ensures superior aesthetic outcomes of the treatment with veneers. In addition to that, composite vs porcelain is inherently stable in terms of color. The staining of laminates is negligible in the long term, which is another advantage of the best veneer material. The whole list of veneer-related issues directly results from the firm bonds that can be formed between the surface of the tooth and this type of veneer. The process of bonding can be performed using the etch-and-rinse approach, or it may take the form of self-etch as well. The success and clinical outcome of adhesive teeth veneers are strongly dependent on managing the constraints of adhesion compatibility between the materials used for composite vs porcelain veneers and the bonding system.
Except for the achieved visual effects, the lifetime of laminates might be counted as another advantage of this type of veneers. When regularly maintained, the service of veneers is stable over time, and the results of clinical studies vary between performance after an observation period of 10 years. It is noteworthy that the clinical success of laminate veneers largely depends on the level of experience and the expertise of the clinicians. As a consequence, some patients may not benefit at all or may benefit less from the properties of laminate veneers due to a lack of tooth reductions necessary when shape and color alteration is desired. Thus, for plenty of clinical situations, a consideration should be made to compare veneers with direct composite.

Unlike laminate veneers, which are built in a dental lab, composite veneers are constructed directly on the surface of the teeth. Composite materials include resin, additives for strength and texture, and pigments. The resin gives the best veneer material plasticity, allowing it to be soft and pliable until it is cured or hardened by the dentist or technician using a UV, LED, or halogen light. The advantage of composites over laminate veneers is that they are more accurate and precise. A complete vision for the shape, surface texture, and color of the veneers enables the dentist to work on extra-fine details and achieve a higher level of naturalness. Composites can be constructed directly on the teeth in one dental visit when they are molded and cured freehand. In-office constructed composite veneers are significantly more affordable than laminate ones, both because of the easily available component material and the shorter treatment time. They are also not as costly to repair and reconstruct. From a dental aesthetics standpoint, composite veneers incorporate various shades, transparencies, and opacities and are readily customizable to match the natural appearance of a patient’s facial profile. Composite veneers, however, are made out of a more porous best veneer material; they are susceptible to staining, yellowing, discoloration, and chipping, but to a lesser extent than direct bonding veneers. Nonetheless, due to the softness of the best veneer material used in direct composite veneers, adjustments or repairs can be made during the veneer’s short-term use. In other words, the durability of composites matches the duration of use of direct veneers.
There are various pros and cons when it comes to laminate vs composite veneers. The first and most important point of analysis is the cost of the materials themselves. The cost of laminate veneers is simply higher than the cost of composite resins. This cost must be conveyed to patients in clinical decision-making. Thus, the first point is to know what the patient has in mind. Both types of veneers have taken part in various research on their longevities. However, the composites used for laminate veneer cementation will certainly affect the long-term retention of laminate veneers. The microstructure of the best veneer material used, either composite or ceramic, will greatly affect the bonding retention of the laminate veneers. Furthermore, from the aesthetic aspect, we know that the natural appearance of the teeth after being restored using laminate veneers has better aesthetics and is more popular than composite veneers. The surface appearance of an object, as it looks aesthetically, is influenced by the viscoelastic properties of the external surfaces of an object or material. The teeth are no different. The surface of enamel on the teeth will affect how natural the shape and color of the teeth look. Finally, the application technique of both veneer options is different. A critical analysis is the vulnerability to chipping from the incisal edge in these veneers. This analysis states that this will depend on the intensity of the activity, functional load, bruxism, or clenching. The primary concerns in both clinical cases are mostly tooth sensitivity after the delivery appointment, chipping, and the staining or discoloration that can be caused by the daily consumption of food.
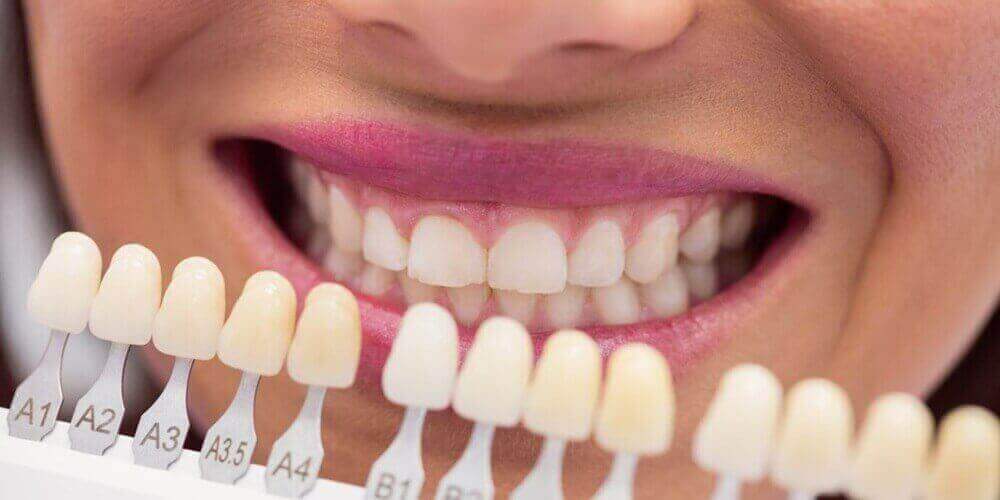
The clinical scenario and the advantages and disadvantages of laminates and composites play a decisive role in choosing the best veneer material used. For the professional to make the best decision, he should know which are the most delicate characteristics for each of the products to be reviewed, submitting the case to the evidence and convenience from the analysis of different perspectives, beyond only technical discussions. After concluding the clinical examination and the appliance, some features of the best veneer material and the desires of the patient should be observed. From this, it is possible to carry out the planning, inform the patient about the expectations, and carry out the treatment. Let us now evaluate some clinical situations that would characterize veneer choice.
The simplicity of use of laminates and their greater longevity may be an important point. In the case of older patients who are undergoing orthodontic whitening treatment that will probably extend into the future and some need to improve their social position, using laminates would not just be beneficial in a supracrestal position. In simpler cases, especially when the color of the teeth is darker, particularly from the gingival region, or when the best veneer material with metallic incrustation is used, laminates would be an excellent indication. Alternatively, in case the treatment has included an implant or a fixed prosthesis either before or during lithotomy, composites would be very convenient. When financial difficulty is part of the case, this client prefers a direct evaluation of only a few units in the lab right out of the mouth. Thus, the composite would also be a good choice for patients in general, as in the previous case. The most varied materials provide excellent results for veneers, and every year there are new polymers and composite varieties that capture the attention of professionals and become part of their armamentarium. This context allows the public to have varied therapeutic possibilities related to dental veneers.